Neural Nets
Since 2006, a set of techniques has been developed that enable learning in deep neural nets (NN). These deep learning techniques are based on stochastic gradient descent and backpropagations. These techniques have enabled much deeper (and larger) networks to be trained.
Deep Neural Network models
Some of the most used deep NN models are:
a) Feedforward NN:
a.1) Multi-Layer perceptron (MLP). [1]
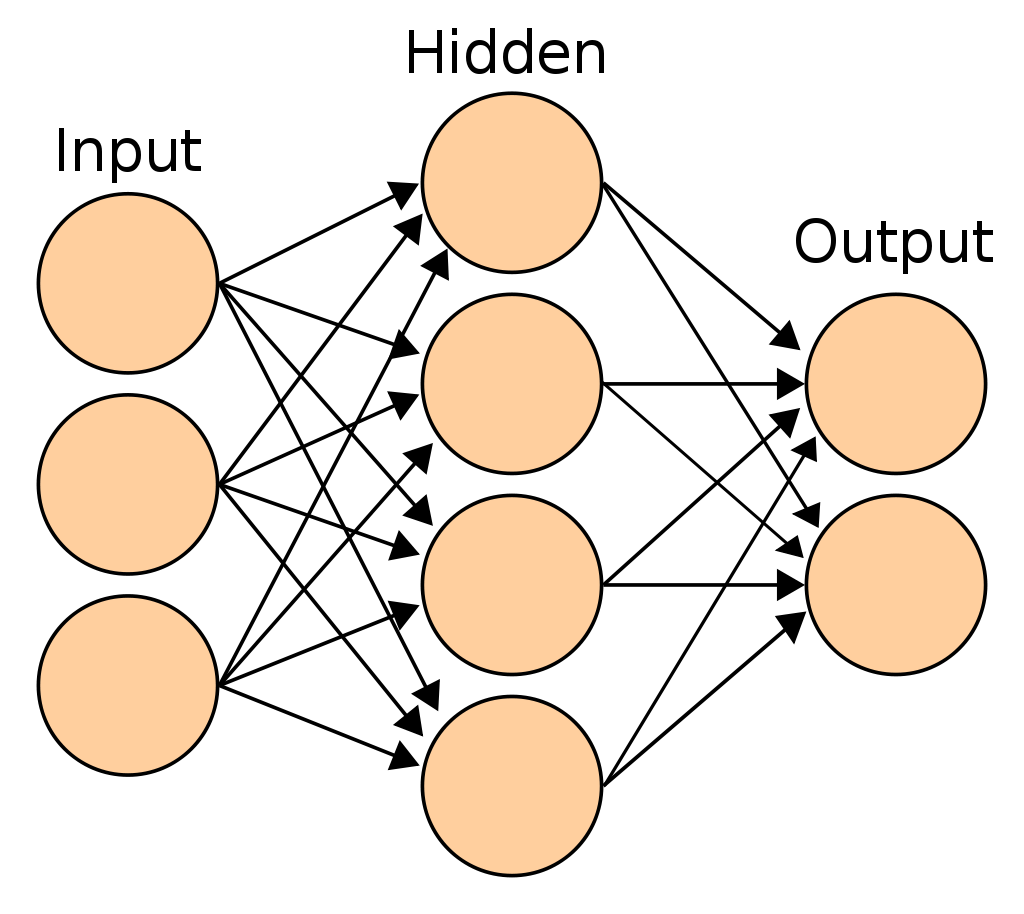
a.2) Convolutional NN (CNN). [2]

a.3) Image to image models {Unet (Encoder-Decoder), GAN, etc.} [3]

a.4) Generative models {GAN (generator vs discriminator), VAE (variational autoencoder), etc }[4]

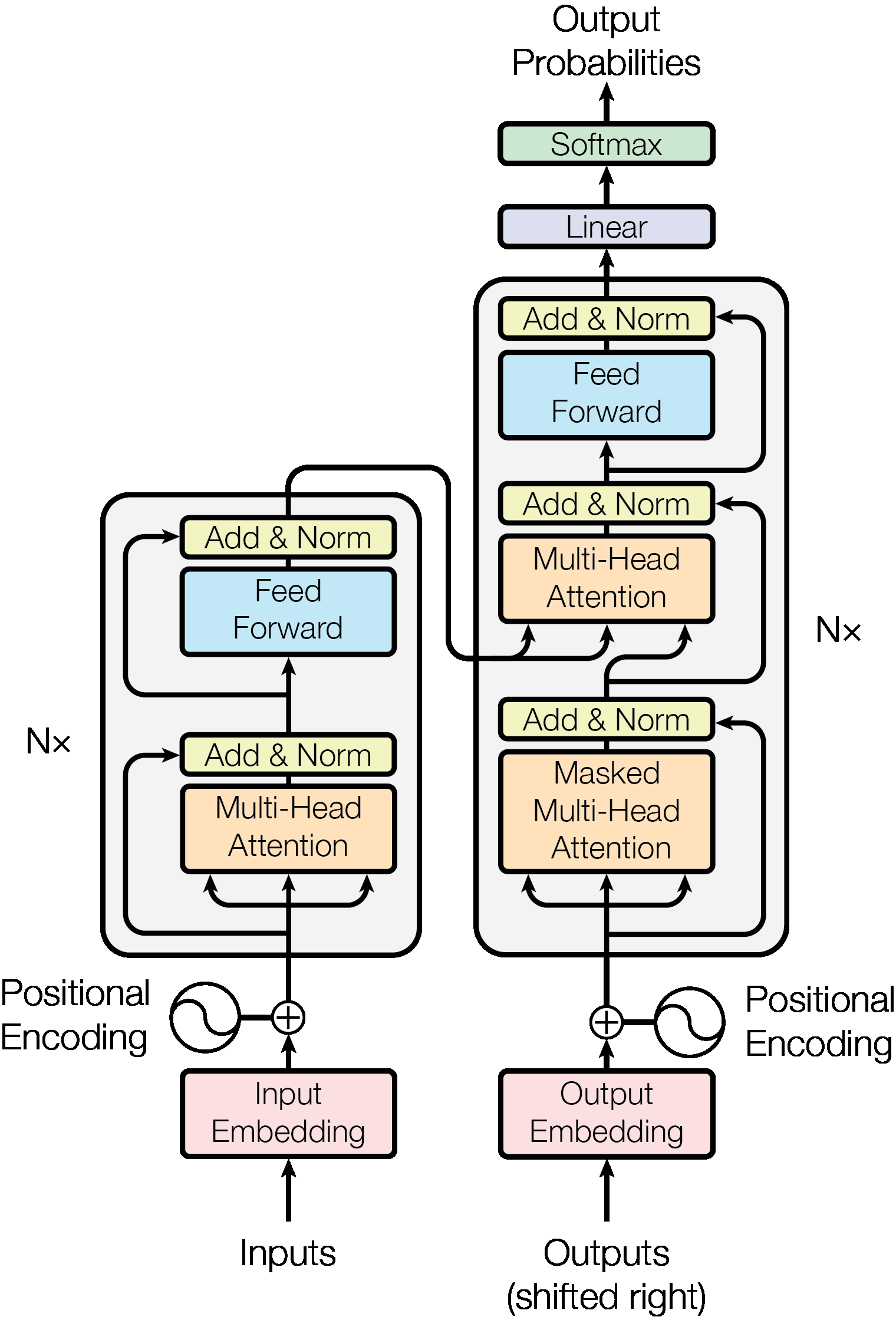
a.5) Transformers. [5]
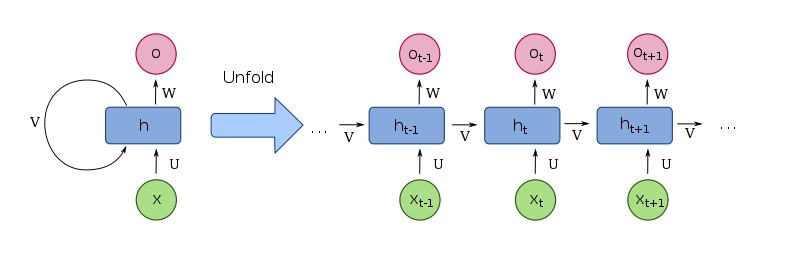
b) Recurrent NN (RNN): applied with time series analysis. [6]
b.1) LSTM.
b.2) GRU.
Data augmentation
The supervised training of deep artificial neural networks requires in some cases a large amount of data. In these cases in which it is difficult to obtain data or labeling them requires a high time and economic cost, different techniques are used to solve this problem. The most common are the use of the transfer learning technique and data augmentation from real data transformations. Another widely used technique is the generation of synthetic data using simulators, which allow perfectly labeled data to be obtained. The major difficulty in synthetic data generation is the domain gap problem.
Applications
We have applied deep neural for solving several C. elegans applications:
- Alive/dead classification [7]

- Detection [8]
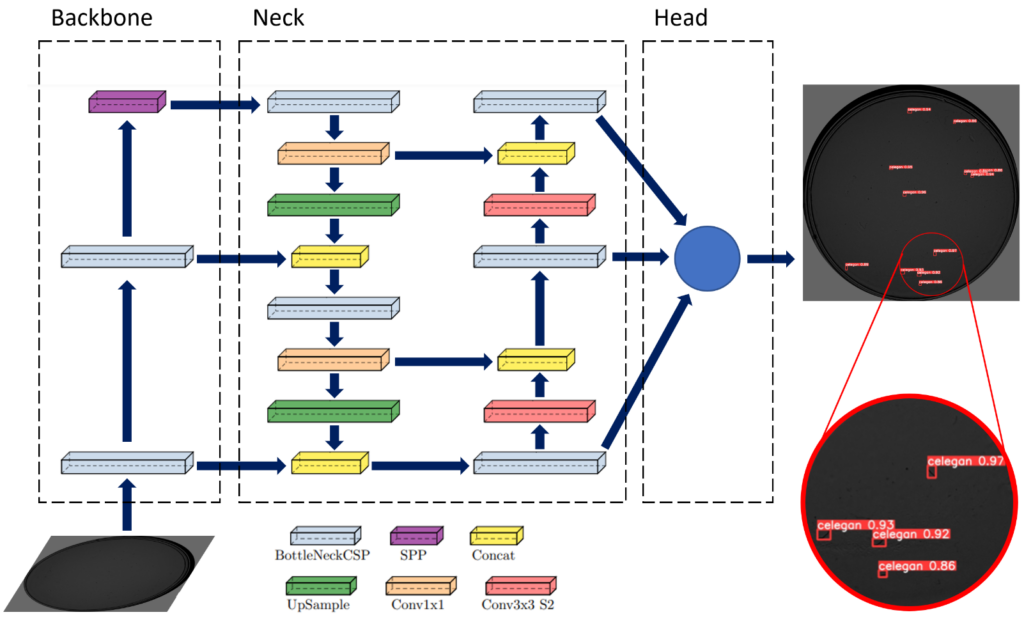
- Skeletonization
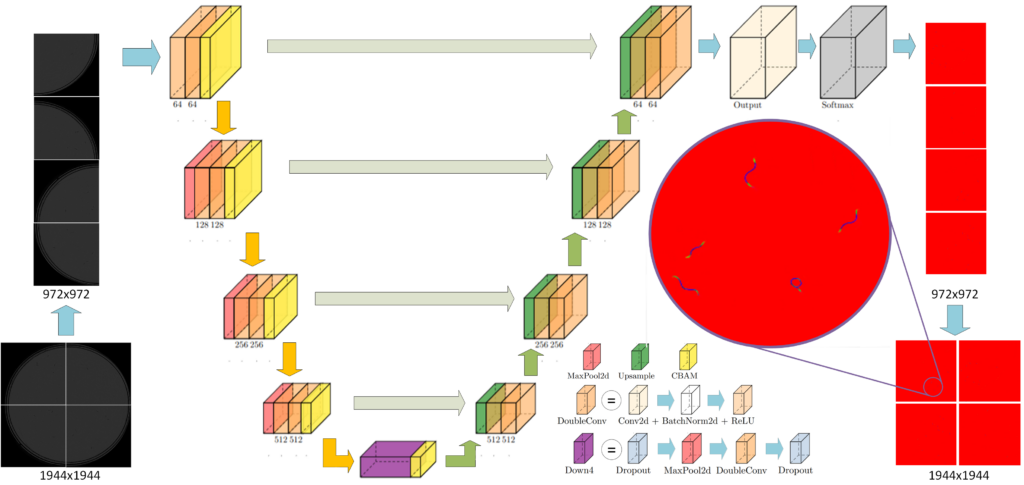
And we have developed data augmentation techniques:

References
[1] https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Artificial_neural_network.svg
[4] https://sthalles.github.io/intro-to-gans/
[6] https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Recurrent_neural_network_unfold.svg?uselang=ca